Creating a fleet to manage dedicated server allocation
Overview
A fleet scales virtual machines, and manages dedicated servers that are hosted within those virtual machines, based on regional scaling configurations.
Goals
After you complete this guide, you should have an understanding of the following:
- How to create a fleet
- What does it mean to activate or deactivate a fleet
- How to tailor make fleets to suit your needs
Prerequisites
Before you begin this guide, you should complete the following:
- Integrate a dedicated server with the AccelByte server SDK.
- Have access to the Admin Portal, and the namespace and account for your game.
- Uploaded a dedicated server build to AMS.
Create a fleet to start up your dedicated game servers
AccelByte Multiplayer Servers (AMS) can start up your dedicated game servers whenever there is demand. However, before AMS can do so efficiently, it needs to have all the necessary data on how best to run your dedicated game servers, as well as where and when to run them. The fleet creation process will ensure that you have given all information required for AMS to manage your fleet.
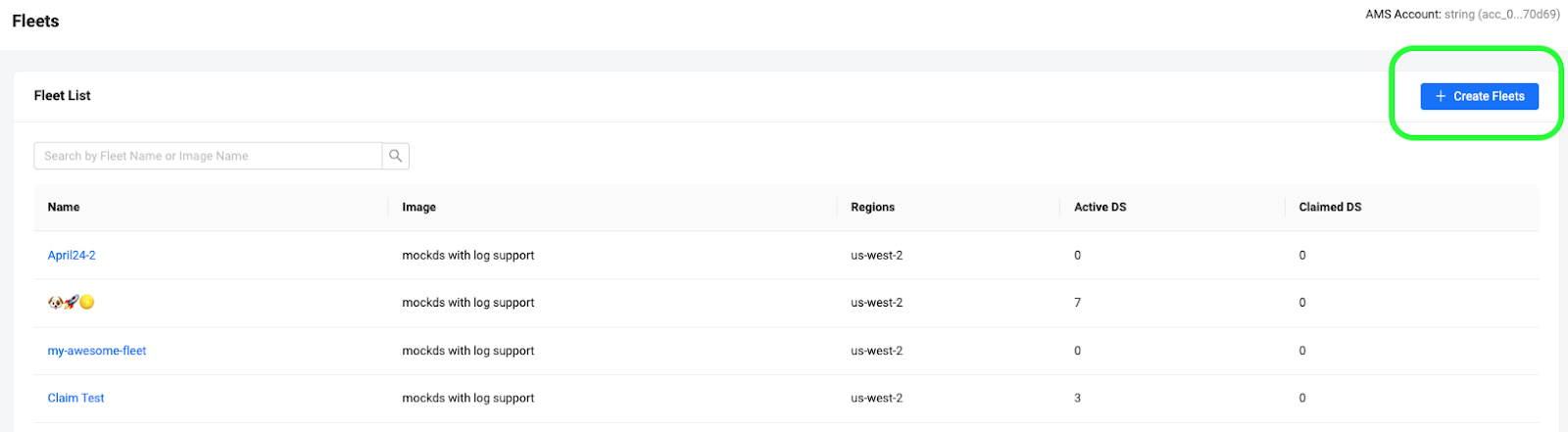
Click the Fleet button that is located under AccelByte Multiplayer Servers, on the side menu bar.
On the subsequent page, click the “Create Fleet” button located at the top right hand corner of the page.
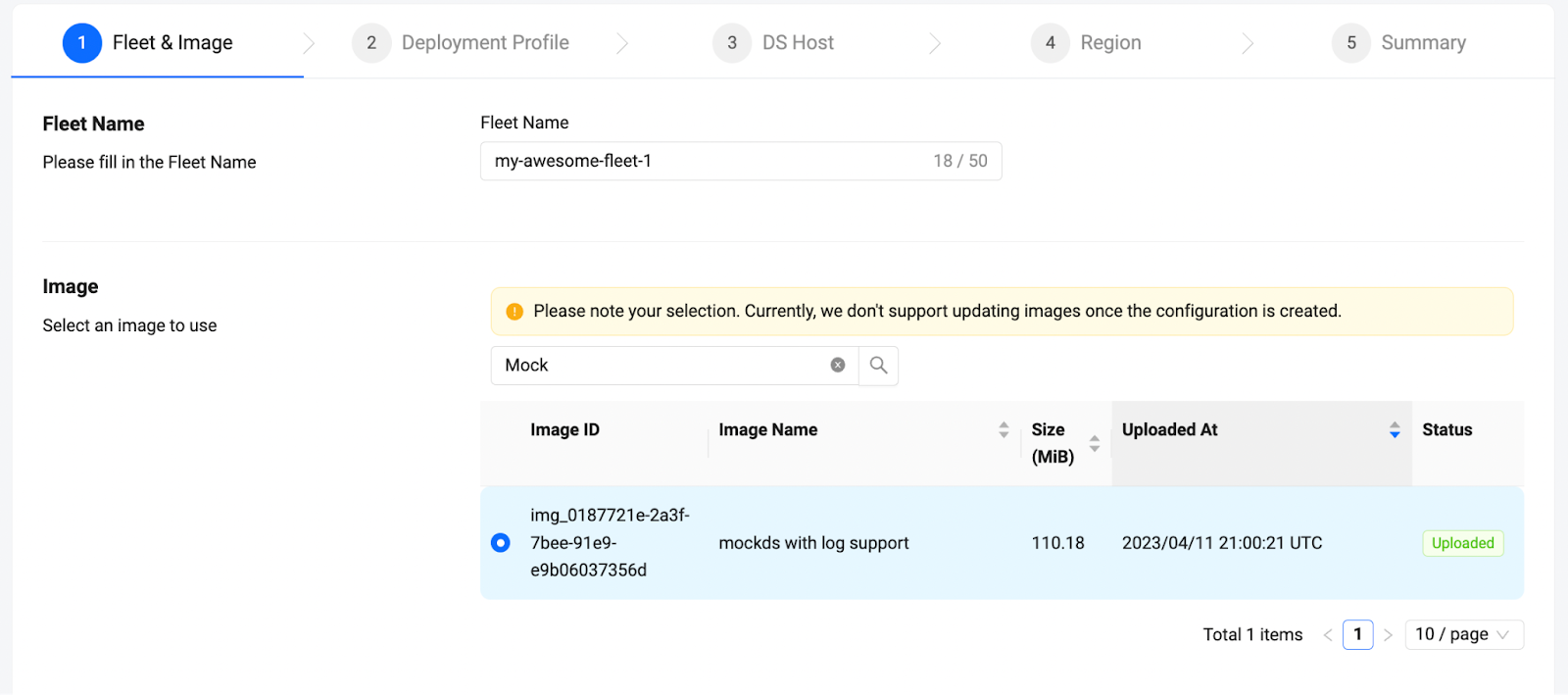
Give your fleet an identifiable name, then choose one dedicated server image that has been uploaded to the account. The fleet will start dedicated servers based on this image.
:::note
- Your fleet name must be unique within the namespace.
- You can search for your image by using its image ID or image name. A partial match is acceptable. :::
- Redefine your time out values if necessary:
- Creation Timeout: The creation timeout starts when the local watchdog executes your dedicated server, and marks its state as Creating. This timeout gives a configurable time limit for your dedicated server to initialize, so that when your dedicated server fails to do so, AMS will remove the server, and return its resources back to the regional cluster.
- The creation timeout is applicable only when the dedicated server is in the Creating state. Once the dedicated server registers itself to the dedicated server manager, it will enter the Ready state.
- The default value for this timeout is 300 seconds.
- Session Timeout: The session timeout starts when the dedicated server starts serving a game session and enters the In Session state. It gives a time limit for your dedicated server to serve a game session, so that watchdog can remove stale servers that fail to exit themselves normally, once a game session has finished.
- The default value for this timeout is 7200 seconds.
- Drain Timeout: The drain timeout starts when the dedicated server receives the drain signal from the local watchdog. This drain timeout tells the dedicated server it is about to be shutdown, and gives a time limit for your dedicated server to do any last minute actions and exit itself before the watchdog forcibly kills it.
- The default value for this timeout is 30 seconds.
- Unresponsive Timeout: The unresponsive timeout refreshes when a server finishes its last health check with AMS. It gives a time limit for your dedicated server to recover the connection to AMS in case of any network interruption. If the timeout is exceeded, AMS can remove the server and recover its resources.
- The default value for this timeout is 300 seconds.
Specify any additional parameters that come after your executable to run your dedicated server. To learn how, see Construct your dedicated server command.
Next, tell the fleet which instance type you want your dedicated servers to run in, and how many servers you want to run in each instance.
The instance type can be searched by its name. If you want additional information on the instance type, click the info button on the entry.
Next, tell the fleets which region you want to host in, and which scaling strategy to use in each region.
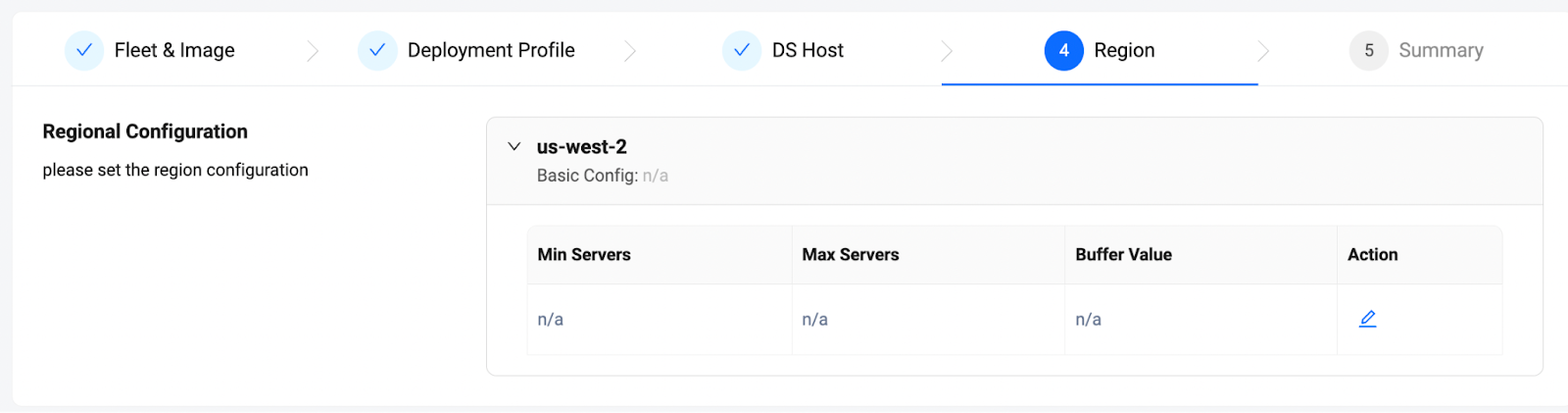
- Scaling strategy is composed by Min Server, Max Server and Buffer Value.
- Min Servers: The minimum number of servers that the deployment needs to maintain, regardless of whether the servers are in the Ready (warmed buffer) or In Session (serving a game session) state. This value is useful to handle the baseline concurrent users, by ensuring that there are enough servers ready to go.
- Max Servers: The maximum number of servers that the region can maintain. This value is useful as a limiter to make sure the cost of game servers will not go over budget.
- Buffer Value: The buffer value tells the fleet the exact number of servers to maintain as warmed buffers.
- Warm buffers are dedicated servers that are idling in the Ready state, ready to be claimed by a game session to start serving the session immediately.
- The fleet will always try to maximize the use of a virtual machine. Therefore, your minimum and maximum number of servers will be rounded up to the closest multiple of the number of servers to run within a virtual machine. This is to make sure there are no wasted resources within a virtual machine that is already billed to your account.
Consider the example where the number of servers to be run in a virtual machine is five, minimum servers is three, and maximum servers is 28. The fleet will adjust the scaling behavior to minimum servers to five 5 and maximum servers to 30. Additionally, if the buffer value results in an additional virtual machine to be requested by the fleet, all five dedicated servers within the newly set up virtual machine will become buffers.
- After you have reviewed all the configurations, click the Create button to create the fleet.
Construct your dedicated server command
Aside from a few required flags, you are free to construct your own dedicated server command. The required flags are as follows:
- Unreal
- Unity
-dsid=${dsid} -port=${default_port} -log=${log_file} -watchdog_url=${watchdog_url}
-dsid ${dsid} -port ${default_port} -logFile ${log_file} -watchdogUrl ${watchdog_url}
-d, -dsid: Dedicated server id
The dsid should be passed into the dedicated server by the flag -d ${dsid} or --dsid ${dsid}. The usage of the flag is covered by the SDK.
-p, -port: Ports
Ports can be passed to the dedicated server with any format of flags that you desire, the substitution variable for your ports will follow the format ${<<your_port_name_in_lowercase>>_port}.
-l, -log: Log file path
The log file path can be passed to the dedicated server with any format of flags that you desire, followed by using the phrase ${log_file} for parameter substitution. Note that you will use the path to emit your logs, so that AMS can carry your logs to the log stash for later retrieval.
-watchdog_url (Unreal), -watchdogUrl (Unity): the URL to the local watchdog
The URL to the local watchdog. The watchdog is the monitoring agent of the dedicated servers in the hosting machine. The SDK will connect to the watchdog automatically using the URL.
Additional variables for substitution
Additionally, AMS supports variable substitution for the following variables in your dedicated server command:
| Variable name | Description |
|---|---|
${creation_timeout} | The value of the creation timeout, as defined in the fleet. |
${session_timeout} | The value of the session timeout, as defined in the fleet. |
${drain_timeout} | The value of the drain timeout, as defined in the fleet. |
${unresponsive_timeout} | The value of the unresponsive timeout, as defined in the fleet. |